|
Location: Jordan TST |
![]()
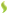 C1 Pharyngitis
C1 Pharyngitis
Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic. Pharyngitis can result in very large tonsils which cause trouble swallowing and breathing. Pharyngitis can be accompanied by a cough or fever, for example, if caused by a systemic infection.
Most acute cases are caused by viral infections (40–80%), with the remainder caused by bacterial infections, fungal infections, or irritants such as pollutants or chemical substances.Treatment of viral causes are mainly symptomatic while bacterial or fungal causes may be amenable to antibiotics and anti-fungal respectively.

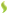 C2 Tonsillitis
C2 Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils most commonly caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Symptoms of tonsillitis include sore throat and fever. While no treatment has been found to shorten the duration of viral tonsillitis, bacterial causes such as streptococcal pharyngitis are treatable with antibiotics. It usually takes one to three weeks to recover.
Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), also extraesophageal reflux disease (EERD) refers to retrograde flow of gastric contents to the upper aero-digestive tract, which causes a variety of symptoms, such as cough, hoarseness, and asthma, among others.
Although heartburn is a primary symptom among people with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), heartburn is present in fewer than 50% of the patients with LPR. Other terms used to describe this condition include atypical reflux, and supraesophageal(or supra-esophageal) reflux.
-
-
* The information is only for reference purposes only , the disease varies from person to person, it is inappropiate to use drugs without doctor's instructions, if you need any assistances or inquiries, please call 31763336

